連接起 改變的力量



你是否還記得當初的夢想?
你所擁有的熱情與創意,無論夢想或大或小,都無比耀眼。




Innovation, Passionate, Daring, Dream.
想要實現這個創意的你,
可能是工程師、創業者、抑或是期待盡情揮灑的夢想家。
Innovation, Passionate, Daring, Dream.
想要實現這個創意的你,
可能是工程師、創業者、抑或是期待盡情揮灑的夢想家。
你們是否正在改變的路上,風雨無阻的前進?
是否在心中期待,有一個人能夠全心全意的給予信任?

在這個瞬息萬變的世界,我們相信
有一群人和我們一樣,懷抱著一個信念 ——
相信行動的力量
相信改變是可能的
Action makes everything possible.


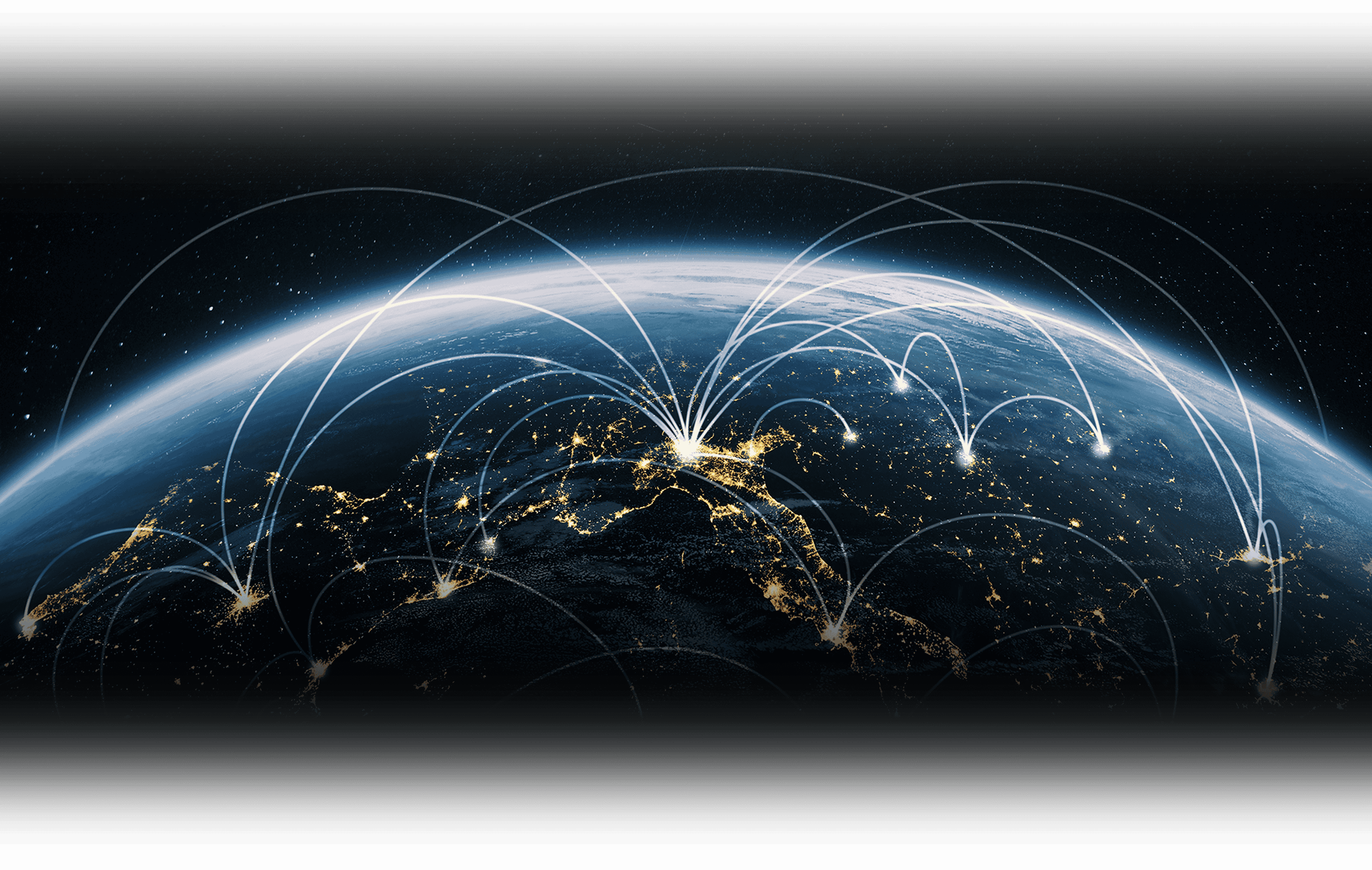
This is where the connector ecosystem begins.
這裡是 連接的開始
This is where the connector ecosystem begins.
這裡是 連接的開始

我們明白,改變並不只是口號
我們選擇用更多的理解,多問一個為什麼
與你共同思考、激盪可能

每一個不能出錯的系統,都建立在看不見的連接點之上
正因如此,我們必須非常可靠
選擇不敷衍、不妥協,選擇解決問題

精密,不只是規格、數值,或者容差
真正的精密,是讓每一個參與者
在同一個節奏上前進
佳楠想要站在,願意行動的人身邊
因為 我們相信
你的火花 值得被世界看見
CONSULT FORM
諮詢清單
查看目前已勾選的諮詢項目,您可透過下方按鈕切換諮詢主題。
DELETE
刪除此項目

此動作將無法復原,請問確定要刪除嗎?
返回前頁
確定刪除
SUBSCRIBE TO NEWSLETTER
訂閱電子報

歡迎訂閱佳楠電子報,我們將會與您分享最我們的最新動態、產品與技術訊息
您的訂閱資訊
返回前頁
若欲取消電子報訂閱,請
點擊此處
SUBSCRIBE SUCCESS
成功訂閱電子報

您已成功訂閱佳楠電子報,敬啟期待我們的最新動態!
確認返回
CANCEL NEWSLETTER
取消訂閱電子報

請輸入您訂閱時所填寫的信箱,我們將協助您取消。
您的訂閱資訊
返回前頁
CANCEL SUCCESS
已取消訂閱

您的電子報已取消訂閱,期待您重新改變心意!
確認返回







